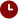
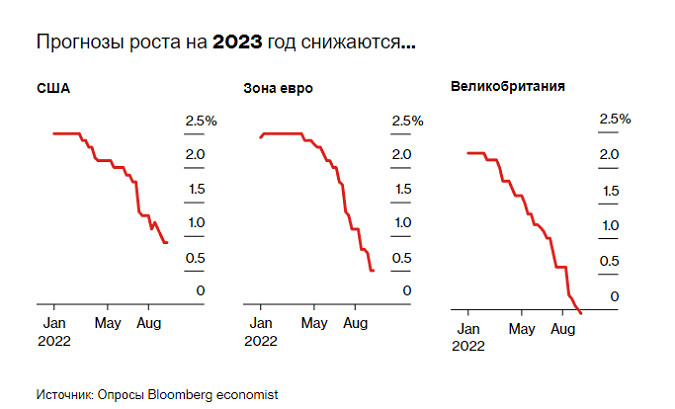
The Federal Reserve and its peers around the world, late in anticipating the worst inflation in four decades and then slow to crack down on it, now make no secret of their determination to win the fight against rising prices - even at the cost of slowing or reducing the growth of their economies.
About 90 central banks have raised interest rates this year, and half of them have risen at least 75 basis points at a time. Many have done this more than once that the chief economist at Bank of America Corp. Ethan Harris calls it "a competition to see who can raise the stakes faster."
The result was the most massive monetary tightening in 15 years, a drastic departure from the era of cheap money that was ushered in by the 2008 financial crisis, which many economists and investors have come to view as the new normal. According to JPMorgan Chase & Co., in the current quarter, the largest central banks will raise rates since 1980, and things will not stop there.
This week alone, the Fed is set to raise its key rate by 75 basis points for the third time, with some calling for a full percentage point after US inflation topped 8% again in August. The Bank of England is forecast to raise its benchmark by 50 basis points, with rate hikes expected in Indonesia, Norway, the Philippines, Sweden and Switzerland, among others.
Putting on the brakes, politicians are beginning to speak grimly, publicly acknowledging that the higher they raise rates to keep inflation in check, the greater the risk that they will hurt economic growth and employment.
Fed Chairman Jerome Powell said last month that his campaign to contain prices "would bring some pain to households and businesses."
European Central Bank Executive Board member Isabelle Schnabel talks about the "sacrifice ratio," jargon for the loss of production it would take to control inflation. The BoE goes so far as to predict that the recession in the UK will begin by the end of this year and could last until 2024.
There is no doubt that monetary medicine will hurt. The question is - how much? Analysts at BlackRock Inc. believe that returning inflation to the Fed's 2% target would mean a deep recession and another 3 million unemployed, while reaching the ECB's target would require even more cuts.
Uncertainty is exacerbated by the delay before the rate hike impacts the economy, in addition to the structure of today's inflation, much of which is due to energy and other supply shocks that central banks cannot control.
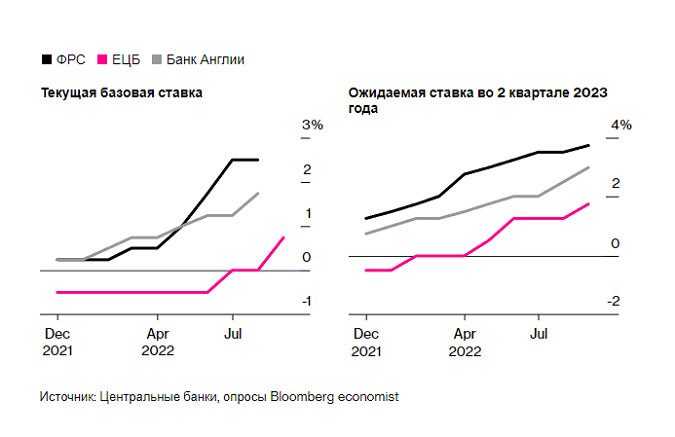
Higher-than-expected US inflation data for August last week sent the stock market into its sharpest drop in more than two years, driven by bets on the Fed's tightening policy. Billionaire hedge fund manager Ray Dalio sees the prospect of more than 20% drops in stock markets as rates continue to rise.
Central banks would prefer their economies to keep chugging along. At some point, they may abandon their aggressive policies to try to ensure this. But now their main goal is to avoid repeating the mistake of the 1970s, when their predecessors prematurely weakened lending in response to the economic slowdown, without first taking inflation under control.
This concern is an argument in favor of moving forward decisively with a rate hike, because if inflation is allowed to rise, it can lead to increased economic problems in the long run.
Anna Wong, chief economist at Bloomberg Economics for the United States, believes that the Fed will eventually have to lower the base rate to 5%, doubling today's level - a dose of further tightening that could cost the economy 3.5 million jobs and deal additional blows to already affected markets.
Powell spent much of 2021 describing the inflation shock as "temporary," and he and his colleagues entered this year predicting that interest rates would need to rise by just 75 basis points in 2022. The Fed has already raised the rate three times more.
Last November, ECB President Christine Lagarde said that a rate hike in the eurozone in 2022 is unlikely, but this month she raised them by 75 basis points and is considering a repeat in October.
This action puts a lot at stake in the fight against inflation.
"Trust is everything for central banks, and it has been undermined by a misunderstanding of temporary inflation," says Rob Subbaraman, chief economist at Nomura Holdings Inc. "Restoring trust in them is their top priority, even if it means dragging out the recession - that's the lesson of the 1970s."
Time lag
In a sign that investors are anticipating a recession in the US, yields on short-term US Treasury securities have risen above their long-term equivalents in most cases this century, with some bond traders betting that the Fed will have to ease policy in the later stages of 2023. Meanwhile, the S&P 500 is approaching its sharpest annual negative since 2008.
One of the reasons for this concern is that monetary policy is working with a lag. First it weakens financial markets, then the economy, and finally inflation. Thus, a repeated increase in rates becomes dangerous.
"It takes time to reduce inflation," says Harris of BofA. "If you start talking about focusing only on current inflation as the main indicator, you will be too late to stop the tightening cycle." Harris believes that the UK and the eurozone will fall into recession in the fourth quarter, as rising energy prices will negatively affect the economy this winter, and he expects a recession in the US next year.
The U.S. economy - and especially the labor market - has been surprisingly resilient so far. But economists say that just means the Fed will have to put in a lot more effort to cool demand.
"Inflation and the labor market have proved more resilient to higher rates than the Fed expected," says former Fed Vice Chairman Donald Cohn, "so they need to raise rates even more now."
Until recently, it seemed to central banks that it would not be difficult to tighten policy. Inflation was sky-high, labor markets were strong, and interest rates were at their lowest.
But the compromises are becoming tougher as high rates begin to take their toll on economies that are already suffering from the effects of a protracted pandemic and the conflict between Russia and Ukraine.
The cost of borrowing in many economies, including the United States, is turning from stimulating to restrictive. A rising dollar is hurting emerging markets with debt. A sharp reduction in Russian natural gas supplies increases the risk of stagflation in Europe, as prices rise amid an impending recession.